Overview of Agriculture Trade Policy, Promotion and Logistics Development Division
Agricultural Trade Policy, Promotion and Logistics Development Division of this Department is entrusted with the responsibility of making policy recommendations on export and import of agricultural commodities. Agricultural Trade Policy, Promotion and Logistics Development Division is the nodal Division of the Department for coordinating/ formulating responses on World Trade Organization’s (WTO) Agreement on Agriculture with the Ministry of Commerce, with DIPP on FDI in agriculture, with Ministry of Finance in matters relating to the modification in the Custom duty and Goods and Services Tax (GST) on agricultural commodities and with Ministry of Commerce in matters relating to Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs)/Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with different countries.
The Division which was earlier called the Agriculture Trade Policy Division has been rechristened as Agriculture Trade Policy, Promotion and Logistics Development Division realizing the importance of Agri-Logistics in improving India’s Agricultural Trade. This Division works in close coordination with the Logistic Division of Department of Commerce and other related agencies for development of agro-logistics.
Work Distribution of Trade Division
I. Formulation of export and import policy recommendations relating to agricultural commodities in coordination with the concerned subject Divisions.
II. Identification of potential foreign markets and agricultural and agro based commodities for export.
III. Formulation/implementation of exports development and export promotion measures.
a) This includes monitoring of market intelligence regarding the commodities in collaboration with subject matter Divisions for purposes of organising export production.
b) Coordination with the Ministry of Commerce regarding export promotion for agricultural commodities. This includes recommendations regarding participation in fairs and exhibitions, sponsoring of Trade delegations, joint ventures in third countries, recommendations on export incentives etc.
IV. Coordination work with respect to the recommendations of Department of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare in respect of Export and Import of Agricultural Commodities.
V. Monitoring Imports of important agricultural commodities keeping in view the interests of the producers/growers.
VI. Coordination with different Divisions in matters concerning policy matter on Foreign Direct Investment.
VII. Coordination with the Ministry of Commerce in taking follow up action on the implementation of GATT/ World Trade Organization Treaty.
VIII. Coordination with various Divisions for suggestions in respect of modifications in custom/ excise duties to be conveyed to the Ministries of Commerce and Finance.
IX. Collection, compilation and analysis of basic data on import/ export, international/domestic prices of agricultural commodities etc.
X. Compilation of information on all bi-lateral/pluri-lateral trade agreements concerning India and identification of commodity-wise market access opportunities available to India as part of these Agreements.
XI. Promotional work pertaining to geographical indications.
XII. Budget proposals including suggestions in respect of modification in customs duties and GST.
XIII. Coordination with the Ministry of Commerce for development of agro-logistics.
3. India’s Agriculture Trade
3.1 Agri-Export:
3.1.1 Export of agricultural commodities has helped producers to take advantage of wider international market which, in turn, has incentivized their domestic production. Crops exported in large quantities viz. rice, sugar, and spices have witnessed significant increase in area coverage and growth rate of production. India has emerged as a significant Agri-exporter in crops likerice, spices, cotton, oil meal cake, castor oil, coffee, cashew, tea, fresh vegetables and sugar.
3.1.2 As per available WTO’s Trade Statistical Review (2022), the share of India’s agricultural exports and imports in the world agriculture trade in 2021 were 2.4% and 1.7%, respectively. India was in the top 10 ranking of the global Agri exporters.
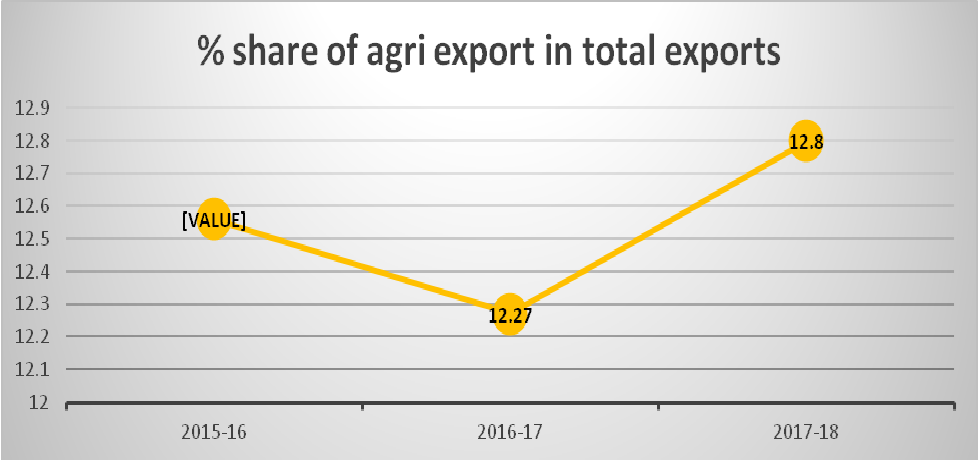
3.1.3 The share of agricultural exports in India’s total merchandise exports was 11.90% in2021-22.
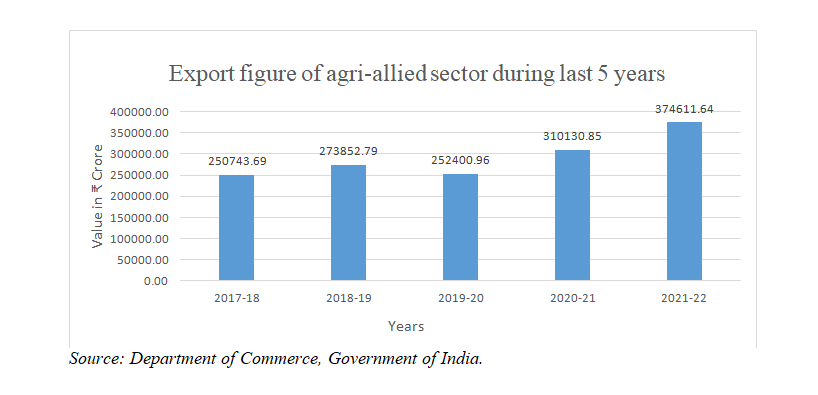
3.1.4 As compared to previous year (2020-21), the Agri and Allied exports in the year 2021-22increased by 20.79% to Rs. 3,74,611.64 crores. The increase in Agri and Allied exports during 2020-21was primarily on account ofincreased exports ofcommodities like Wheat (279.71%), Dairy Products (98.40%), Guergam Meal (71.41%), Sugar (66.17%), Cashew Nut Shell Liquid (64.84%), Other Cereals (56.00%), Cotton Raw Incld. waste (50.39%), Milled Products (48.54%), Coffee (42.59%), Misc Processed Items (36.11%) and Pulses(36.66%), which witnessed high growth in the year 2021-22 as compared to previous same period.
3.1.5 Major destinations of exports for India’s Agri and Allied commodities were Bangladesh, United States of America, China, Vietnam, United Arab Emirates, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, Malaysia, Nepal, Egypt, Sri Lanka, Netherlands, Iran, Iraq,United Kingdom, Japan and Thailand.
3.1.6 The export of Agri-allied sector during last 5 years is as below:
3.1.7 India’s top 10 agricultural export commodities (in terms of value) for the year 2017-18 to 2021-22are given in the Table-1 below:

3.2 Agri-Imports:
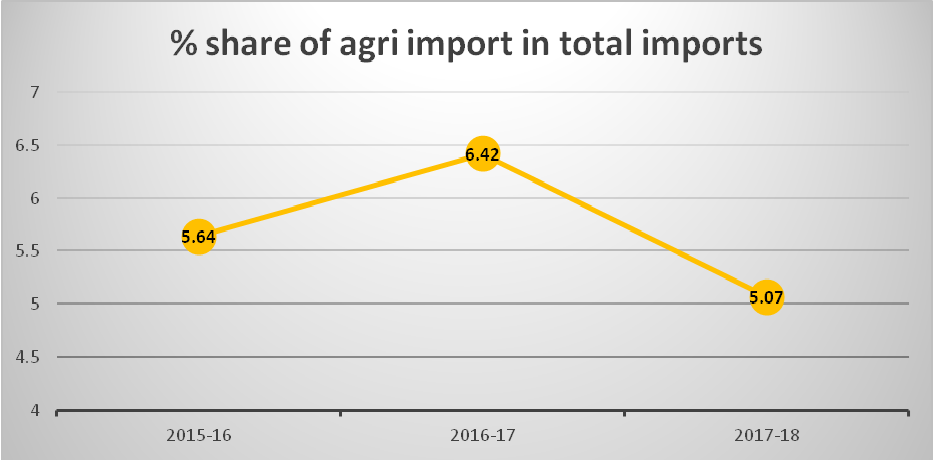
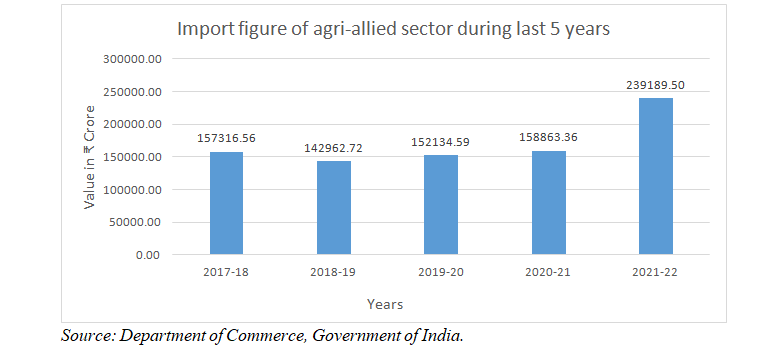
3.2.1 As compared to previous year (2020-21), the Agri and allied imports in the year 2021-22 increased by 50.56%to Rs239189.50 crore. Increasein value of Agri and Allied imports during 2020-21were primarily on account of increase inimports of Vegetables Oil (72.34%), Fresh Fruits (16.35%), Pulses (39.29%), Spices (20.00%), Cashew (24.66%), Natural Rubber (66.73%), Oil Meals (346.33%), Other Oil Seeds (98.94%), Cotton Raw Incld. Waste (45.72%), Misc Processed Items (50.15%), Cocoa Products (34.27%), Cereal Preparations (26.04%), Coffee(17.07%), Processed Fruit and Juices (50.51%), Jute Raw (150.66%), etc. Similarly, the total merchandise imports increased more significantly, therefore the share of Agri and Allied imports has decreased from 5.45% in 2020-21 to 5.23% in 2021-22.
3.2.2 Major sources of import of India’s Agri and Allied commodities are Indonesia, Malaysia, Argentina,Ukraine, United States of America, Brazil, Nepal, Thailand, Myanmar, Singapore, Afghanistan, Tanzania,Vietnam, United Arab Emirates, Bangladesh, China, Canada, Netherlands, Sri Lanka and Australia.
3.2.3 The import of agri-allied sector during last 5 years is as below:
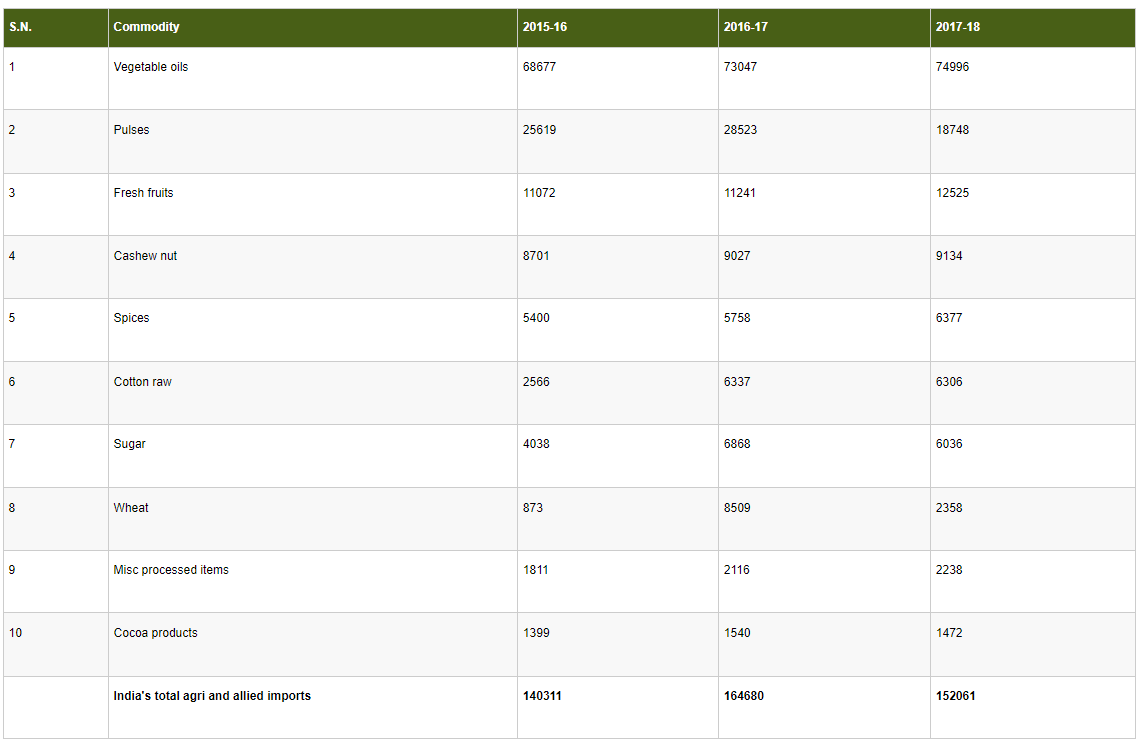
3.2.5 India’s top 10 agriculture import commodities in terms of value for the year 2017-18 to 2021-22are given in the Table 2 below:

3.2.6 Share (in value terms) of top 10 exported and imported agricultural commodities during 2021-22. Agriculture sector posted positive balance of payment like earlier years. The import was dominated bysingle commodity namely vegetableoil.
Import share in 2021-22 (Top-10 Items) Export share in 2021-22 (Top-10 Items)

4 Goods and Services Tax
4.1 GST envisages a single tax on supply of goods and Services or both, by amalgamating all the central indirect taxes (excise duty, countervailing duty and service tax) and state indirect taxes (VAT, luxury tax, entry tax, octroi, etc).
4.2 GST rates on most of the raw agricultural items are at 0% (zero per cent). Apart from this, most of the agricultural activities and services are also exempted from imposition of GST. However, for primary processed agriculture items, GST rate is 5% and for secondary/tertiary processed products, the GST rate is 12%. On some farm machinery/component and fertilizers, the GST rate is in the range of 12-18%.
4.3 Considering the representations/inputs from various stakeholders/firms/associations/farmers etc, this Division has been taking up GST related issues with the GST council, Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance from time to time.
5. Trade Agreement:
5.1 FTA/CECA/CEPA/CECPA
5.1.1 Free Trade Agreements/ Preferential Trade Agreements/ Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreements/ Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements / Comprehensive Economic Cooperation &Partnership Agreements provide opportunities for exports with the trading partners at preferential duties. India has signed agreements with number of regional trading blocs/ countriesnamely, South Asia Free Trade Area (SAFTA), Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA), Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN), Afghanistan, MERCOSUR (trade block of countries viz. Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay), Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand, Bhutan, Nepal, Chile, and Sri Lanka. The recently concluded Trade agreements are with UAE and Australia.
5.1.2 The trade agreement negotiations with European Union, Thailand,BIMSTEC, Peru, Israel, Iran, Mauritius, New Zealand, Canada, UK, Korea and Indonesia are also in various stages of discussion.
6 WTO Meetings/Notifications:
6.1 WTO Meeting: The Committee on Agriculture oversees the implementation of the Agreementon Agriculture. Its key responsibility is to monitor WTOmember’s complianceto their commitments/obligations. The committee, composed up of all WTO members, usually meets three or four times a year. Officers of Trade Division participate in the Meetings of the Committee on Agriculture (CoA) at World Trade Organisation in Geneva, Switzerland. Issues related to India’s Pulses Policy, short-term loan, inputs subsidies and Minimum Support Price (MSP)were responded in coordination with Department of Commerce. Officials will also participate in Ministerial Conference in WTO in 2021.
6.2 WTO Notifications: As part of India’s commitments to the WTO, India needs to notify any new or modified domestic agricultural support measures applied by India during a year and this needs to be notified to the WTO on an annual basis in the form of Domestic Support-1 and Domestic Support-2 Notifications. In this regard, DA&FW has provided requisite inputs to Department of Commerce for preparation and filing of India’s DS notification to WTO. The filed/submitted notifications are available online and can be assessed at the WTO website http://agims.wto.org/.
6.3 Trade Policy Reviews under WTO: WTO conducts Trade Policy Review of its members at regular intervals with a view to reviewing member country’s trade policies and practices under multilateral trade disciplines, to make an assessment of compliance with country obligations. India’s last Trade Policy Review was held in 2020. The review is an extensive exercise requiring inter-ministerial coordination and detailed preparation. The submission of report is followed by detailed question answer sessions which requirecompilation ofhuge trade related documents/data.DA&FW is required to furnished relevant inputs/information to Department of Commerce for compilation and forwarding to the WTO Secretariat as a part of India’s Trade Policy Review (TPR) at WTO.
7. Strengthening India’s Agri Export –Creation of Agri-Cells in nations abroad At the insistence of DA&FW, Agri-cells were created, by Ministry of External Affairs, in 15 Indian Missions viz., Vietnam, USA, Bangladesh, UAE, China, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Malaysia, Japan, Nepal, Indonesia, Argentina, Singapore, Ukraine and Brazil to help bring focus on agricultural exportsand optimize potential available in those countries for Indian products. The Agri Cells also compile information on demand supply of various commodities in the host countries which could be utilized by the exporters.
8 Export Promotion Forum (EPF):
8.1 Product specific Export Promotion Forums (EPF) for eight agri products i.e. Grapes, Mango, Banana, Onion, Rice, Dairy Product, Pomegranate and Floriculture have been created by DOC under the aegis of APEDA at the insistence of DA&FW. They will work on promoting the export of identified potential products in a focused manner.
8.2 Each Export Promotion Forum is having exporters of the related commodity as its members along with official members from DOC, DA&FW and MOFPI along with relevant expert institutions and State Governments. Presently, Chairman APEDA is the chairman of each of these forums. The forums are required to meet regularly to discuss/ make recommendations on issues pertaining to export of the respective commodity and invite experts etc. to the meeting for interaction, as required. The Forums will constantly monitor and identify/anticipate developments in the external/internal situation pertaining to the production and export of their respective commodity and recommend /intervene for taking the necessary policy/ administrative measures.